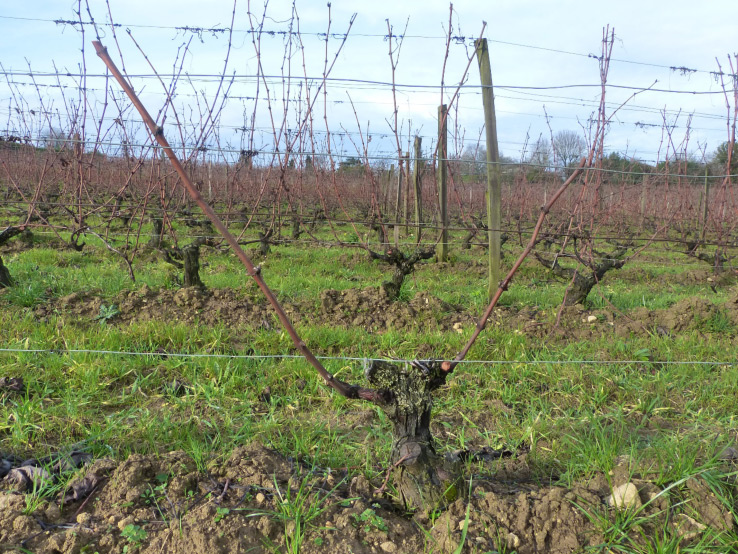
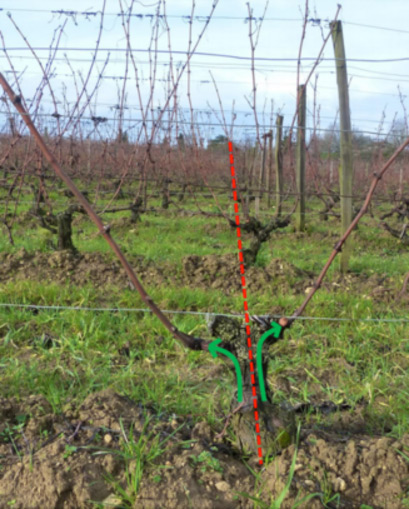
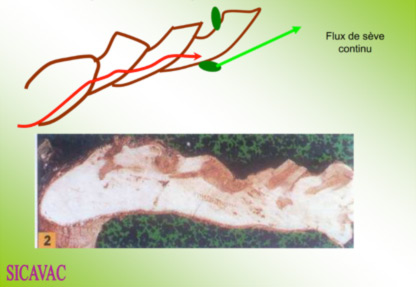
Gestion du palissage et surface foliaire dans les pays chauds
Gestion du palissage et surface foliaire dans les pays chauds Dans les pays chauds la conduite de la vigne se fait par rapport à la faible disponibilité en eau et aux risques liés au soleil. Au cœur de l’été, les températures peuvent dépasser les 40°C plusieurs jours...